User Guide
This section provide a guide to configure Scorpion 2DScanner.
The scanner has the following properties:
Multiple area scan cameras can be connected
Each connected camera have these feature
resampler, optional, clipping, resampling or both
filter, optional, shading correction or custom filter
image FIFO buffer, optional
The camera images are stitched together
Each camera can be shading corrected
Each camera can be 2D or 3D calibrated
A 3D calibrated 2Dscanner is a 3D Scanning device
The stiching with 3D calibration is superior to 2D
Working with stiching of multiple cameras 3D calibration is in the essence
The 2DScanner resamples and receive each camera in a separate thread. Moving resampling to the 2DScanner improves performance, ease of use and abstraction.
It will also increase the latency and possibly decrease the framerate
Image flow
The image flow from cameras to the final scanner image consist of several steps
acquisition - fetching image from camera
resampling - resampling, either clipping or resample to calibrated image
filter - filtering of resamplet image from camera
stitching - inserting partial image into the final scanner image matrix - row/column
Resampling
The incoming image may be clipped and/or resampled by a an external calibration file. The calibration file is typically created by Scorpion calibration profiles. Resampling is performed in SVLResample.dll.
Resampler options is name of calibration file, absolute path or relative to 2DScanner.ini.
Filter
A filter may be applied to the resampled image from camera as the second processing step. The filter is applied to the resampled image before stitched into the final outgoing image. Currently a ShadingCorrection and CLAHE filter is available in SVLImageFilter.dll version 1.0.0.6 or newer.
ShadingCorrection uses a calibration imagefile acquired of a grey surface/calibration sheet using the same cameras as the 2DScanner. The calibration file must be of same size as the resampled image. Recommended fileformat same as target cameras.
In cases where the calibration file is of other format than the raw image from camera, the camera target format may be specified in FilterOptions.
If resampling is not used, the calibration file must be of same size as the raw image from camera.
ShadingCorrection FilterOptions -t<targetvalue> -f<fmt> -g<gain> -o<offset>
-f <filtertype> - currently ShadingCorrection (f - FlatField) and CLAHE (h) is supported
Flatfield filter options
The FlatField filter, also known as ShadingCorrection, is used to correct uneven illumination or shading in images. This filter applies a calibration image to normalize the intensity across the image. The calibration image should be acquired under uniform lighting conditions using the same camera setup as the 2DScanner. The FlatField filter equals STC-0172-ShadingCorrection.
The following options are available for the FlatField filter:
-t<targetvalue>: Specifies the target pixel value for scaling the calibration image. If omitted or set to 0, the maximum pixel value in The calibration image is used. The target value should be in the range <0..255>.
-f<fmt>: Defines the format of the camera image. If omitted, the format defaults to the calibration file format, mono or rgb. Supported formats include:
bgra: Common 32-bit color format used by libraries like arrlib, numpy, and Windows, rarely used by cameras
rgba: Rarely used 32-bit color format.
bgr: Common 24-bit color format used by cameras and 24 bit bitmap files
rgb: Rarely used camera format, used by JPEG files.
gray: 8-bit grayscale format. May be used if calibration file is a color image to convert to gray as the camera.
-g<gain>: Applies a scaling factor to each pixel after shading correction. The gain value must be greater than 0, with a default of 1.0.
-o<offset>: Adds an offset to each pixel after shading correction. The offset value can range from -256 to 255, with a default of 0.
Note
The calibration image must match the size of the resampled image if resampling is used. If resampling is not used, the calibration image must match the size of the raw camera image.
Proper calibration ensures accurate shading correction and improves the quality of the final stitched image.
Calibration files should be of .bmp files, .jpg may change image pixel content due to compressing.
CLAHE (Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization)
CLAHE is an advanced image processing technique used to improve contrast in images, particularly for local regions. It is an extension of standard Adaptive Histogram Equalization (AHE).
Unlike standard Histogram Equalization (HE), which applies a transformation based on the global image histogram, AHE and CLAHE divide the image into small, non-overlapping regions (called tiles). For each tile, a separate histogram is computed, and the contrast is locally enhanced based on that region’s histogram.
The key improvement in CLAHE is the Contrast Limiting mechanism, which prevents the over-amplification of noise that can occur in AHE, especially in uniform or dark regions. This limiting is achieved by clipping the histogram at a predefined value (the clip limit) before equalization. The clipped portions are then uniformly redistributed across the histogram bins.
This results in a more natural-looking and noise-suppressed contrast enhancement compared to global HE or standard AHE.
The following options are available for the CLAHE filter:
-l<cliplimit>
Description: This is the threshold for contrast limiting. Any histogram bin count exceeding this value will be clipped, and the excess will be distributed among other bins.
Impact: A higher value allows for higher contrast enhancement, while a lower value provides greater noise suppression and a more subdued effect. A typical default might be
40.0.
- -s<tileGridSize> (
tuple of two integers, e.g.,(8, 8)) Description: Defines the size of the grid (or tiles) into which the image is divided. The tuple represents
(M, N), where M is the number of tiles along the horizontal axis and N is the number of tiles along the vertical axis.Impact: A smaller grid size (more tiles) results in more localized contrast enhancement but can increase processing time. A larger grid size results in a more global enhancement effect. A typical default is
(8, 8).
- -s<tileGridSize> (
Stitching
Each subimage is put into a matrix of column due to camera index and row due to no of stripes in final scanner image. If timeout if used and the time expires, the missing columns is filled with static pixel values.
Installation
The 2DScanner SCD - Scorpion Camera Driver is a virtual camera driver
Installed by the Scorpion Vision Installer.
Use like any other camera driver
Has no GUI
Is configured directly using the 2DScanner.ini file
Multiple 2DScanners can be installed in a profile.
The Scorpion Camera drivers used is specified in the configuration file.
Configuration file
The configuration file 2DScanner.ini is located in the Scorpion profile’s Hardware folder. If missing, create the file manually by using a appropriate example from this documentation.
The inifile has multiple sections
Config - common section
Scanner<nnnn> - individual scanner 1..n configuration
Scanner<nnnn>.Camera<n> - individual scanner n’s camera configuration
Note
There are samples of the configuration file at the end of this guide
Config Section
Common setup for all scanners in the config file
Key |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|
CameraDriver |
<driver.dll> |
name of Scorpion Camera Driver for actual cameras attached - SCD |
FilterDLL |
SVLImageFilter.dll |
name of Scorpion Standard filter dll |
ResampleDLL |
SVLResample.dll |
name of Scorpion Standard Resampling dll |
ResampleMode |
0 |
|
Verbose |
0 |
|
Note
CameraDriver must be the same for all cameras connected to a 2DScanner
Example: HVGrab_1_0_4_46.dll - it is required that the SCD SDK is installed
Note
ResampleMode is default bilinear=0 which provides the best resampling - other modes may improve scanning rate
bilinear is the most accurate resampler
nearest neighbour is the fastest
The ResampleDLL - SVLResample.dll is distributed in Scorpion - not adviced to change.
Scanner<nnnn> section
Common setup for all cameras for a single scanner, Scanner<nnnn>. Values in the common section are used for this scanner’s camera values if omitted in the individual camera section.
Key |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Cameras |
1 |
Number of ‘horizontal’ camera images in stitched image |
Scans |
1 |
Number of ‘vertical’ scans in stiched image |
ActiveGrabTimeout |
0 |
Timeout period in milliseconds between triggers or images. |
MinScans |
0 |
Minimum scan count to accept the image when a timeout occurs. |
Overlap |
0 |
Number of scans overlap copied to the next image |
Scale_x |
1.0 |
‘vertical’ scale of each camera image, defaults to 1 (not yet implemented) |
Scale_y |
1.0 |
‘horizontal’ scale of each camera image, defaults to 1 (not yet implemented) |
TopLeft_x |
0 |
Top left corner x offset in object coordinates relative to calibration (0,0) when calibration file is used, else offset in pixels |
TopLeft_y |
0 |
Top left corner y offset in object coordinates relative to calibration (0,0) when calibration file is used, else offset in pixels |
Size_x |
100 |
Resamling height of final image in object coordinates or pixels |
Size_y |
100 |
Resamling width of final image in object coordinates or pixels |
Angle |
0 |
ROI angle in degrees |
Pitch_x |
1.0 |
Pixelsize x in outgoing image |
Pitch_y |
1.0 |
Pixelsize x in outgoing image |
PassThru |
<empty> |
Index of raw images to pass thru to Scorpion while scanning. - will disable passtrhru should be empty in runtime systems |
Active |
0 |
Active or passive image defines if the raw image should be passed before or after stitched image when scan is complete. If Active, the stitched image is passed to application before the origin, else after stitched image. NOTE! applies to images in PassThru list only. |
Threaded |
1 |
Threaded resampling. May be turned off for small images/short resampling time. |
Note
When multiple cameras, ie. stitching each ‘stripe’ horizontally, the TopLeft_y for next camera is by default TopLeft_y+Size_y of previous camera, assuming each camera is calibrated to same origin (0,0).
Each parameter Scale / TopLeft / Size / Pitch / Threaded may be overriden for each camera by inserting the keys into the corresponding Scanner<nnnn>.Camera<n> section, see later examples.
When using camera specific calibration file for each camera, TopLeft should be set in each camera section.
Note
Overlap used to created overlapped images
Useful when individual objects are scanned on a conveyor.
The overlap defines the partial scan images or scans to be copied to the next images.
Note
PassThru a python inspired comma separated list of indexes
“0” passes all.
‘’ or ‘-’ to disables passthru.
“1,-1” equals first and last image in scan is passed to scorpion.
disable when running fast rumors of a memory leak
Negative values are from end of the list
should be empty and disabled in runtime systems
Note
MinScan applies when ActiveGrabTimeOut > 0
If MinScans>0
MinScans is number of scans allowed missed.
If no of scans is less than MinScan on timeout, current partial scan is discarded.
If MinScans=0
All timeout scan are silently discarded
Useful when two images are required to be in sync - eg Stereo Vision
Scanner<nnnn>.Camera<n> section
Individual setup for each scanners camera. The file is located in the profiles hardware folder.
Resampling and Filtering
Resampling input image by using a pose2D calibration file from Scorpion. The calibration file contains both intrinsic and extrintric characteristics of the camera. Typically the calibration file is generated by a separate Scorpion calibration profile using the same camera and configuration used by the 2DScanner. The calibration defines a origin with coordinates (0,0). The resampler ROI topleft and size is relative to the origin point, and given in object coordinates.
In cases where the calibration is done on a sub image of the raw image, the same sub image may be specified by the crop offset and size parameters in the 2DScanner configuration file. The offset and size must be set according the sub image used in the calibration profile.
Key |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Port |
0 |
Cross index to physical camera’s port number, 0-indexed |
Fifo |
0 |
Number of images delay before sent to Scorpion. Useful when the stitched image contains the same object captured by two ore more cameras at different time. Requires triggging of cameras due to object movement, typically HW trigged by encoder or similar. While filling up the fifo, partial images from this camera in the complete stitched image will be black (pixel value 0). See reset command for resetting the fifo. |
ImageFilterArgs |
Filename of shading correction image, empty if no filter is used. The file image must be of same size as the output from resampler if calibrated, else same size as camera image. |
|
ImageFilterOptions |
-t0-g1.0-o0 |
Targetvalue, gain and offset. Gain as float +/- 1, offset in +/- pixel value added after applied gain. |
CalibFile |
Name of calibration file for actual camera. Running scanner in pixel mode, ie without calibration, set Calibfile to empty or pixels. Calibfile must be set with absoulte path or relative to this file’s location. TopLeft and Size must be set according to calibration file. |
|
CropOffset_x |
0 |
Resampler topleft pixel offset x in raw input image (integer) |
CropOffset_y |
0 |
Resampler topleft pixel offset y in raw input image (integer) |
CropSize_x |
0 |
Resampler crop size height in pixels (integer) |
CropSize_y |
0 |
Resampler crop size width in pixels (integer) |
Centers |
Dynamic ROI centers, a list of round-robin center postions of format (x0,y0),…,(xn,yn). Optional. May be used for stitching of moving objects. The center point index is incremented round-robin for each image indepenent of the Scans parameter. The center point index is reset on scanner reset command. Centers overrides single TopLeft_x and TopLeft_y parameters. |
|
Angles |
Dynamic ROI rotation, a list of round-robin angles in format a0,…,an. Optional. The angle index is reset on scanner reset command. Angles override single Angle parameter. |
Note
FIFO is a buffer to delay the camera images to sync with other cameras before stitching
This can be used to synch images in time when they are captured in different position
Useful to reduce time difference when camera positions differs
Note
Multiple calibration height/levels may be added by duplicating Scanner<nnnn>.Camera<n> sections and postfixing Scanner<nnnn>.Camera<n>.Calib<c>, where <c> is 1 to max calibrations.
Copy actual keys different from parent section Scanner<nnnn>.Camera<n> and modify for actual calibration height.
Calibration height may be set by modifying property calib, See examples for a configuration sample.
Note
Shading correction and calibration files are relative to the 2DScanner.ini directory.
Calibration files are normally located in the Scorpion profile’s Calibration/2D folder
Swithing between calibration files may be set by setProperty(“Calib”,index)
Filter options where changed in version 1.0.0.27 - see release notes
Note
Dynamic ROI, Centers and Angles parameters, increases the resampling time for calibrated systems. For none calibrated systems, where ‘resampling’ works in pixelmode with angle 0, moving ROI centers have no resampling overhead.
Note
Recommended port numbering:
Port=0 for camera 1
Port=1 for camera 2
Duplicates might cause confusion
Example 1 : Dynamically changing calibfile
Changing calibration when configuration contains multiple calibrations, typically multiple calibration heights.
cam = GetCamera('Scanner0001') # get scanner
cam.setProperty('Calib',1) # switch to calibration #1
Resampler and Filter properties
Property |
Access |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
camera<n>.resampler.active |
R |
boolean, enabled resampling |
|
camera<n>.resampler.height |
R |
single scan height in pixels |
|
camera<n>.resampler.width |
R |
single scan width in pixels |
|
camera<n>.resampler.calibfile |
R |
string, accessible by executeCmd |
|
camera<n>.filter.active |
R/W |
boolean, enabled filtering |
|
camera<n>.filter.targetvalue |
R/W |
0 |
calibration image scaling value, calibmax is used if set to 0 |
camera<n>.filter.calibmin |
R |
min pixel value in calibration image |
|
camera<n>.filter.calibmax |
R |
max pixel value in calibration image |
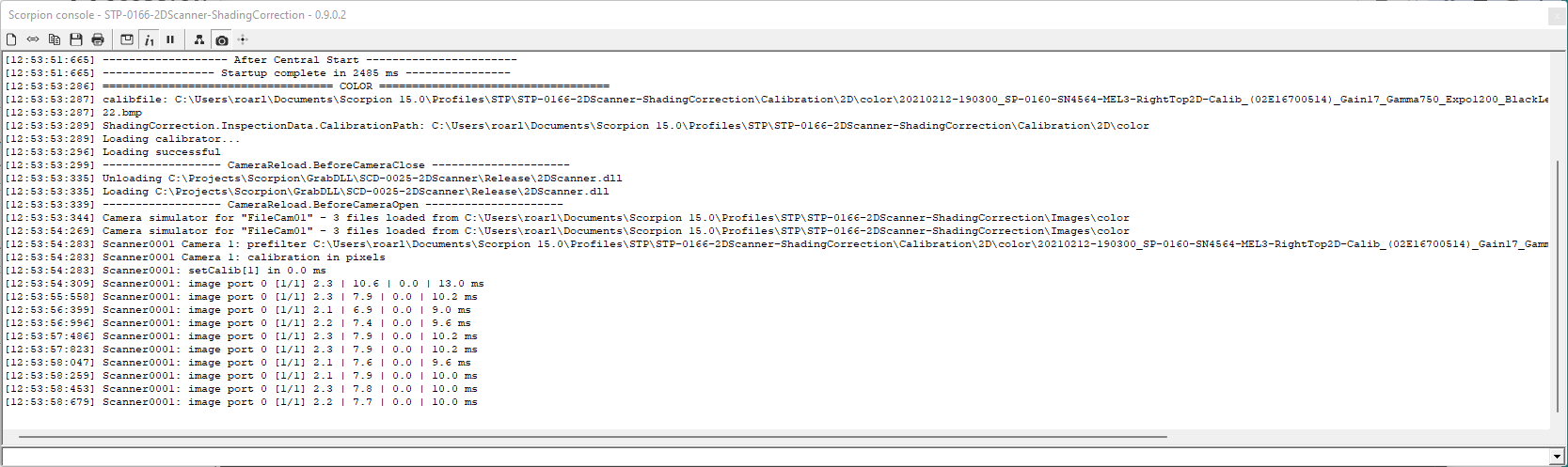
Console window with verbose messages
Note
Setting camera properties via scanner synchronizes properties for all attached cameras and is very useful and faster than accessing each camera.
Any camera property can be accessed with scanners setProperty.
Getting camera properties must be accessed individual, either from actual camera or
cam = GetCamera('Scanner0001') #get the scanner camera
cam.setProperty('exposure', 1000) #set continous for all attached cameras
Supported properties
Properties may be accessed by either Scorpion commands or Python camera interface. Cameras attached the scanner may be accessd by prefixing property name by camera<1..b>, i.e “camera1.exposure”
Property |
Access |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
scanCount |
R/W |
1 |
configuration value |
calib |
W |
0 |
set index of optional calibration files for all cameras |
minScanCount |
R/W |
0 |
configuration value |
activeGrabTimeout |
R/W |
0 |
configuration value ms |
overlap |
R/W |
0 |
configuration value |
count |
R/W |
current scans in buffer. After completed scan, count is set to 0. By setting count>1 copies the previous scans to top creating an image overlap. |
|
pixelsize |
R |
8 |
mirrored value from camera |
width |
R |
total image width |
|
height |
R |
total image height |
|
passthru |
W |
1 |
set partial image passthru, see PassThru configuration. Set to outside scanCount range to disable passthru. |
scanTime |
R |
total time from first image received until scan complete (ActiveGrabTime) |
|
trigTime |
R |
average trigger period of last scan |
|
activeGrabTimeoutCount |
R |
no of timeouts since initied |
|
cameras |
R |
no of configured cameras |
|
verbose |
R/W |
0 |
print messages to console, 0=None, 1=debug If verbose, for each image received, a console message will be generated, showing time consumption of operations performed
|
camera<n>.<prop> |
Access attached camera property |
Supported commands
Commands may be sent to scanners via Scorpion Python camera interface.
Command |
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|---|
reset |
fill=value fifo=1 |
reset scan counters. If optional fill parameter is given, image buffer will be set to value, else kept unchanged. Optional fifo=1 resets fifo for scanners attached cameras. |
trig |
fill=value |
force trig even if scan is not complete. Remaining scans are filled with value if specified, else data is kept unchanged |
clear |
fill=value |
clear image buffer for uncomplete scans. If fill parameter is given, pixel value will be set to value, else 0 |
stat |
prints scanner status to console |
|
set |
prop=value |
access to any property, including properies supported by setProperty |
get |
prop=name |
returns property value as string, including properties supported by getProperty and following special properties camera<n>.resampler.CalibName camera<n>.filter.Args camera<n>.filter.Options |
Examples - properties
Example 2a - Set 2DScanner Properties for all cameras
cam = GetCamera('Scanner0001') #get the scanner camera
cam.setProperty('continous', 1) #set continous for all attached cameras
cam.setProperty('exposure', 1000) #set exposure for all attached cameras
Example 2b - Get property enumerated with cameraN
exposure = cam.getProperty('camera1.exposure', 1) #get specific camera
Example 2c - Get property using GetCamera(name)
exposure = GetCamera('0').getProperty('exposure') # equals above
Example 2d - Set 2DScanner Properties
cam = GetCamera('Scanner0001')
cam.setProperty('scanCount', 6)
cam.setProperty('activeGrabTimeout', 6)
Examples - scripts
Example 3a - executeCmd(‘get’,’value=imageStatus’) for Scanner0001 and 0002
def imagestatus():
cameras = (‘Scanner0001’,’Scanner0002’)
for cam in cameras:
print cam,GetCamera(cam).executeCmd('get','value=imageStatus')
# output
[10:41:13:950] Scanner0001 {'imageCount': 2061, 'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 0,'activeGrabTime': 1577, 'trigTime': 65, 'camera0': {'imageCount': 49464, 'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 0}}
[10:41:13:950] Scanner0002 {'imageCount': 2061, 'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 0,'activeGrabTime': 1577, 'trigTime': 65, 'camera0': {'imageCount': 49464, 'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 0}}
Example 3b - executeCmd(‘get’,’value=imageStatus’))
def imagestatus(): # multiple cameras connected to scanner
print 50*'-'
status = eval(GetCamera('Scanner0001').executeCmd('get','value=imageStatus')) # imageStatus is returned as a string
print 'imcnt:',status['imageCount'], 'aGrabTimeoutCnt:',status['activeGrabTimeoutCount'],
print 'activeGrabTime:',status['activeGrabTime'], 'trigTime:',status['trigTime']
print 'cam1:',status['camera0']
print 'cam2:',status['camera1']
print 'cam3:',status['camera2']
# output
imcnt: 1855 aGrabTimeoutCnt: 0 activeGrabTime: 1891 trigTime: 210
cam1: {'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 2, 'imageCount': 16707}
cam2: {'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 2, 'imageCount': 16707}
cam3: {'activeGrabTimeoutCount': 2, 'imageCount': 16707}
Example 3c - executeCmd(‘stat’)
print GetCamera('Scanner0001').executeCmd('stat') # prints stats to console
# output to console
Scanner0001: last scan 1657 ms, avg trig period 184 ms
Image count 690 timeout count 0
Cam[1] image count 0 total 6218 timeouts 1
Cam[2] image count 0 total 6218 timeouts 1
Cam[3] image count 0 total 6218 timeouts 1
Example 4 - executeCmd(‘reset’,’fill=0’)
cam = GetCamera('Scanner0001')
cam.executeCmd('reset','fill=0')
Example 5 - setProperty(‘verbose’,1) - will output scanner information
The verbose property is good for seeing the details of the image flow
def verbose():
cam = GetCamera('Scanner0001')
if cam.getProperty('verbose') == 0:
cam.setProperty('verbose',1)
else:
cam.setProperty('verbose',0)
# sample output
[09:36:55:311] Scanner0001.0 [1/8] 2.7 | 5.1 | 0.0 | 8.0 ms
[09:36:55:311] Scanner0001.1 [1/8] 0.3 | 5.2 | 0.0 | 5.7 ms
[09:36:55:312] Scanner0001.0 [2/8] 0.2 | 4.6 | 0.0 | 5.4 ms
[09:36:55:312] Scanner0001.1 [2/8] 0.2 | 5.1 | 0.0 | 5.5 ms
* * * * * *
1 2 3 4 5 6
* 1 - image source
* 2 - partial counters
* 3 - transfer time
* 4 - resamling time
* 5 - filter time
* 6 - total processing time